Epoxy resin is a versatile and widely used material in various industries, from electronics to construction. One of the key properties that makes epoxy resin valuable is its insulating properties. In this detailed and comprehensive article, we will explore the characteristics of epoxy resin as an insulator, its applications, and the factors that influence its insulating performance. We will also discuss the advantages and limitations of using epoxy resin as an insulator in different contexts.
Understanding Insulators
Before delving into the specifics of epoxy resin as an insulator, it’s essential to understand the fundamental concept of insulation and the role of insulators in various applications. Insulators are materials that inhibit the flow of electrical current, preventing the transfer of electric charge between conductive materials. They play a crucial role in electrical systems by ensuring safety and preventing unintended electrical discharge or short circuits.
Properties of a Good Insulator
A good insulator should possess certain key properties to effectively perform its function. These properties include:
- High Resistivity: A high-resistivity material restricts the flow of electrical current, making it an excellent insulator.
- Low Dielectric Constant: A low dielectric constant minimizes the ability of a material to store electrical charge, reducing capacitive effects in electrical circuits.
- Thermal Stability: Insulators should withstand a range of temperatures without degrading or losing their insulating properties.
- Mechanical Strength: Insulators should be mechanically robust to endure environmental and operational stresses.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistance to chemicals and environmental factors ensures the longevity of the insulating material.
Epoxy Resin as an Insulator
Epoxy resin is a polymer that exhibits several properties that make it suitable for use as an insulator in various applications. Let’s explore these properties in detail:
- High Resistivity: Epoxy resins typically have a high resistivity, making them effective insulators. This characteristic ensures that they can inhibit the flow of electrical current.
- Low Dielectric Constant: Epoxy resins have a relatively low dielectric constant, which means they have minimal capacitance effects, making them useful in applications where low capacitive coupling is essential.
- Thermal Stability: Epoxy resins exhibit good thermal stability and can withstand a broad range of temperatures without losing their insulating properties. This makes them suitable for both high-temperature and low-temperature applications.
- Mechanical Strength: Epoxy resins are known for their excellent mechanical strength, providing protection to the components they insulate. This property ensures the longevity and reliability of the insulation.
- Chemical Resistance: Epoxy resins are resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for use in harsh environments where exposure to chemicals is a concern.
Applications of Epoxy Resin as an Insulator
Epoxy resin’s insulating properties have led to its widespread use in various industries and applications:
- Electronics: Epoxy resin is commonly used for encapsulating and insulating electronic components, such as printed circuit boards (PCBs), to protect them from moisture, dust, and environmental factors. It also provides electrical insulation between components.
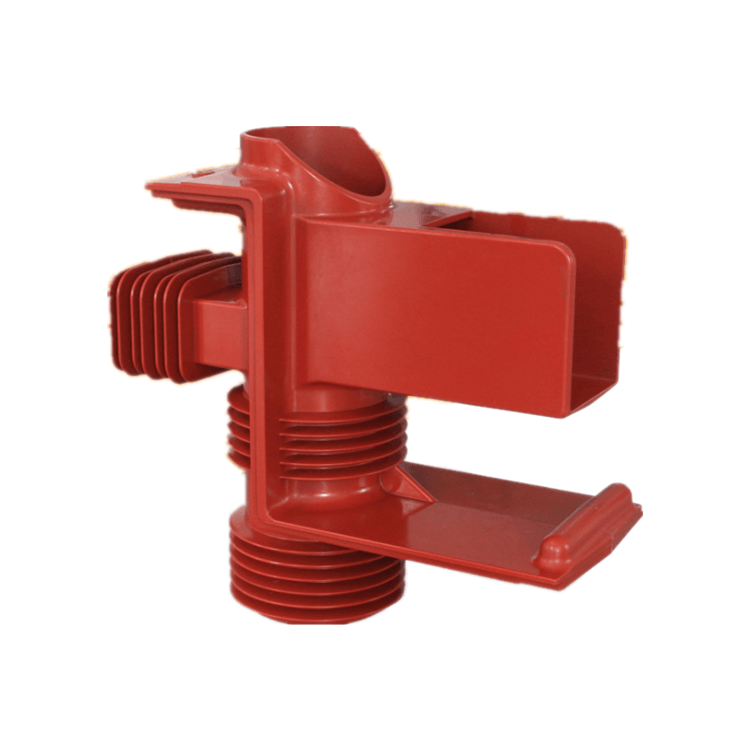
- Power Distribution: Epoxy resin is used in high-voltage insulators and bushings for power distribution systems, where it plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the electrical grid.
- Transformer Insulation: Transformers use epoxy resin as an insulating material to separate the windings and ensure efficient energy transfer.
- Coating and Potting: Epoxy resin is used to coat or pot electrical components, offering both electrical insulation and mechanical protection.
- Aerospace and Automotive: Epoxy resin is utilized in aerospace and automotive applications, providing insulation in critical components and wiring harnesses.
Factors Influencing Epoxy Resin’s Insulating Performance
The insulating performance of epoxy resin can be influenced by several factors:
- Composition: The specific formulation of the epoxy resin, including additives and curing agents, can affect its insulating properties.
- Thickness: The thickness of the epoxy resin layer used for insulation can impact its ability to inhibit electrical current.
- Environmental Conditions: Epoxy resin’s performance may be affected by exposure to temperature variations, humidity, and chemicals in its operating environment.
- Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation and adhesion to the substrate are essential for effective insulation.
Advantages of Using Epoxy Resin as an Insulator
Using epoxy resin as an insulator offers several advantages:
- High Performance: Epoxy resin provides excellent electrical insulation, ensuring the safe operation of electrical and electronic systems.
- Durability: Epoxy resin is known for its longevity, even in demanding environments, which reduces maintenance and replacement costs.
- Versatility: Epoxy resin can be tailored to meet specific application requirements by adjusting its formulation and curing conditions.
- Chemical Resistance: Its resistance to chemicals makes epoxy resin suitable for use in a wide range of industries.
- Environmental Friendliness: Epoxy resins are often considered environmentally friendly as they produce minimal emissions and can be recycled.
Limitations and Considerations
While epoxy resin is a valuable insulating material, it is essential to consider its limitations and potential challenges:
- Cost: High-quality epoxy resins can be relatively expensive, particularly when customized formulations are required.
- Curing Time: Epoxy resins may require specific curing conditions and time, which can impact production schedules.
- Application Complexity: Applying epoxy resin as an insulator requires expertise in handling and curing the material to ensure proper insulation.
- Compatibility: Compatibility with other materials and substrates must be considered to avoid any adverse reactions.
Conclusion
Epoxy resin is indeed a good insulator, given its high resistivity, low dielectric constant, thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Its versatility and effectiveness have made it a popular choice in a wide range of applications, from electronics to power distribution. However, its performance can be influenced by factors such as composition, thickness, and environmental conditions, and careful consideration of these variables is essential for optimal results. While epoxy resin offers many advantages, including durability and chemical resistance, it is essential to weigh these against the potential limitations and costs. In summary, epoxy resin’s role as a reliable insulator remains pivotal in ensuring the safety and efficiency of various electrical and electronic systems.