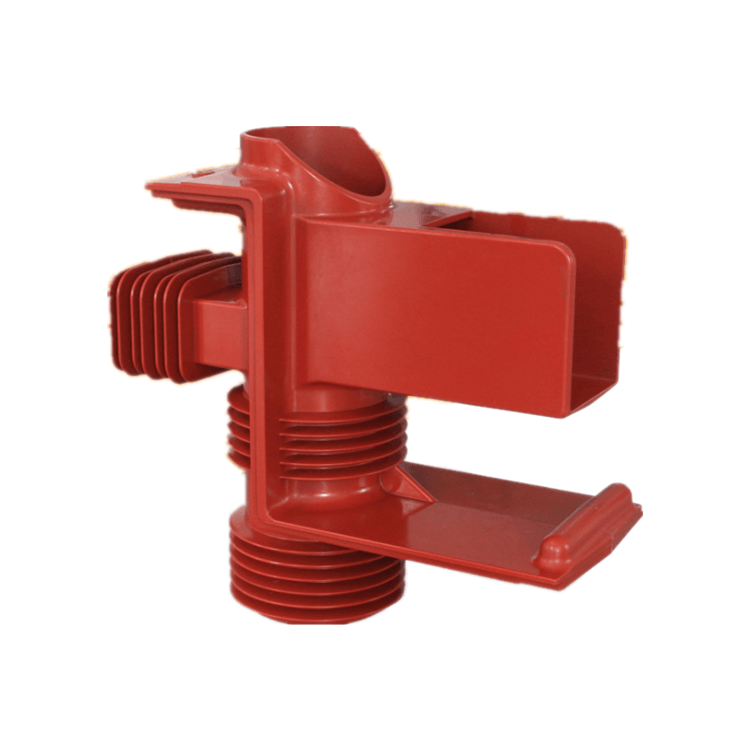
Epoxy insulators and epoxy bushings are critical components in electrical power systems, widely used for their superior electrical and mechanical properties. This comprehensive guide aims to provide in-depth knowledge about epoxy insulators and bushings, covering their design, applications, manufacturing processes, advantages, and maintenance. Understanding these essential components is crucial for ensuring the reliable transmission and distribution of electrical power.
Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Epoxy Insulators
1.1. Insulator Basics
- Definition and purpose of insulators in electrical systems
- Role of insulators in preventing electrical leakage and flashover
1.2. Epoxy as an Insulator Material
- Properties of epoxy resins
- Dielectric strength and electrical insulation characteristics
- Thermal and mechanical stability
1.3. Types of Epoxy Insulators
- Pin insulators
- Disc insulators
- Post insulators
- Suspension insulators
Chapter 2: Epoxy Insulator Design and Manufacturing
2.1. Design Considerations
- Voltage and current ratings
- Environmental factors (e.g., pollution, UV resistance)
- Mechanical strength and load-bearing capacity
2.2. Epoxy Insulator Components
- Core materials
- Shed design
- Fittings and hardware
2.3. Manufacturing Processes
- Molding and casting techniques
- Curing and post-processing
- Quality control and testing
Chapter 3: Epoxy Bushings: Types and Applications
3.1. Epoxy Bushings Overview
- Definition and purpose
- Insulating properties in electrical equipment
3.2. Types of Epoxy Bushings
- Oil-filled epoxy bushings
- Dry epoxy bushings
- Condenser bushings
3.3. Epoxy Bushing Applications
- Transformers
- Circuit breakers
- Instrument transformers
- Switchgear
Chapter 4: Advantages of Epoxy Insulators and Bushings
4.1. Environmental Benefits
- Low maintenance requirements
- Long service life
- Minimal impact on landfill waste
4.2. Electrical Performance
- Improved pollution performance
- High tracking resistance
- Enhanced resistance to partial discharge
4.3. Mechanical Strength
- High load-bearing capacity
- Resistance to mechanical and thermal stress
Chapter 5: Installation and Maintenance
5.1. Installation Guidelines
- Proper handling and storage
- Mounting and fixing methods
- Clearances and spacing requirements
5.2. Routine Inspection and Maintenance
- Visual inspection
- Cleaning and pollution mitigation
- Diagnostic testing methods
5.3. Troubleshooting and Repairs
- Common issues and their causes
- Repair or replacement options
Chapter 6: Case Studies and Real-World Applications
6.1. High Voltage Substations
- Epoxy insulators in GIS and AIS substations
- Case studies of successful implementations
6.2. Wind Power Generation
- Use of epoxy insulators in wind turbine generators
- Benefits in offshore and onshore applications
6.3. Railway Electrification
- Epoxy insulators for railway overhead lines
- Improved reliability and safety
Chapter 7: Future Trends and Innovations
7.1. Nanotechnology and Epoxy Insulators
- Advancements in nanocomposites
- Enhanced insulation properties
7.2. Smart Epoxy Insulators
- IoT integration for condition monitoring
- Predictive maintenance
7.3. Environmental Sustainability
- Development of eco-friendly epoxy materials
- Recyclability and environmental impact reduction
Conclusion
Epoxy insulators and epoxy bushings are indispensable components in modern electrical power systems. This comprehensive guide has provided a thorough understanding of their design, manufacturing, applications, advantages, and maintenance. As technology and materials continue to advance, these critical components play a pivotal role in the efficient and sustainable distribution of electrical power. Understanding their principles and applications is essential for power system engineers and professionals in the field.