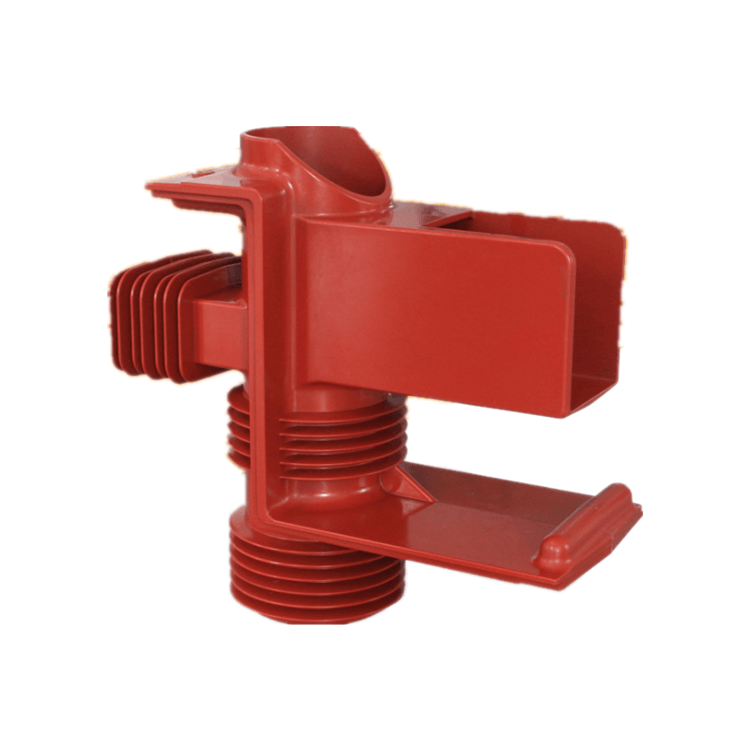
What is the Contact Box/Spout Insulator?
In the realm of electrical power transmission and distribution systems, insulators play a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and reliable delivery of electricity. Contact Box and Spout Insulators are specialized components that contribute significantly to the performance and safety of power distribution networks. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of these insulators, exploring their design, function, materials, applications, and the critical role they play in maintaining the integrity of electrical systems.
Introduction to Insulators in Electrical Systems
Insulators are fundamental components of electrical systems, acting as barriers to prevent the flow of electric current between conductive materials, such as conductors and support structures. In essence, they provide electrical insulation, protecting people and equipment from electrical shocks while maintaining the integrity of the power distribution network.
Contact Box and Spout Insulators are a subset of insulators, each with its own design and applications. These insulators are designed to address specific challenges encountered in power distribution, particularly when it comes to managing electrical clearances and ensuring uninterrupted service.
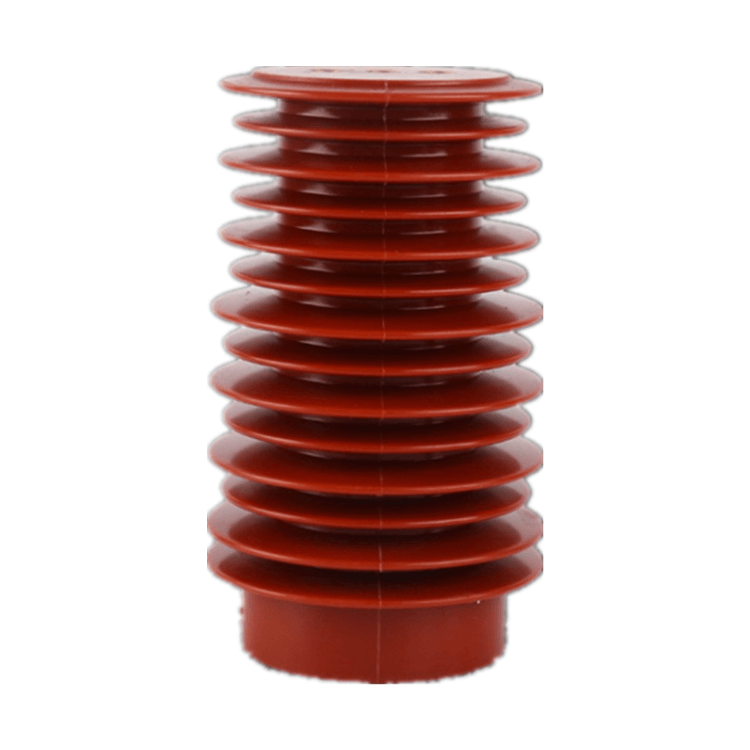
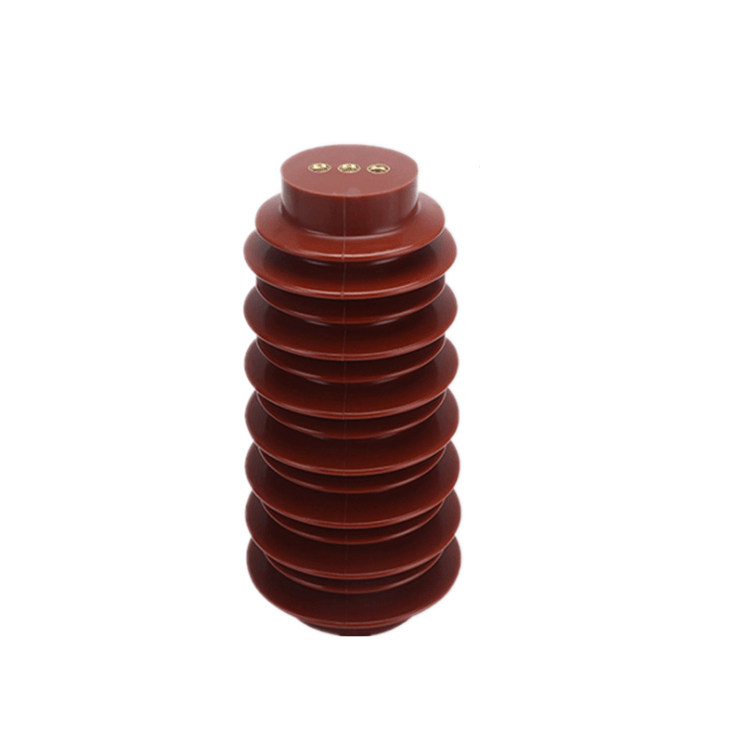
Contact Box Insulators
Contact Box Insulators are designed to provide insulation and support in electrical power systems, ensuring the safe and reliable transmission of electricity. They feature a unique design that includes a box-shaped housing and typically a set of contact points or fittings. Let’s delve into the key aspects of Contact Box Insulators:
Design and Construction
The design of Contact Box Insulators involves a weather-resistant housing, typically made of materials like porcelain or composite polymers. The housing encloses the insulating core, which may be constructed from materials such as glass, ceramics, or composite materials.
Contact points or fittings are strategically placed on the insulator’s surface, providing secure attachment points for electrical conductors. These contact points are essential for maintaining electrical clearances and facilitating the secure connection of conductors.
Function and Applications
Contact Box Insulators serve several critical functions in electrical power systems:
- Electrical Insulation: The primary function is to prevent electrical current from flowing between the conductor and the supporting structure, ensuring safety and system integrity.
- Mechanical Support: They provide mechanical support for conductors, helping to maintain the appropriate distance between the conductor and the supporting structure, even under heavy loads or adverse weather conditions.
- Corona Suppression: The design of these insulators can help suppress corona discharge, which can cause power losses and radio interference.
Contact Box Insulators find application in medium and high voltage power transmission and distribution lines, substations, and other electrical systems where reliable insulation and support are essential.
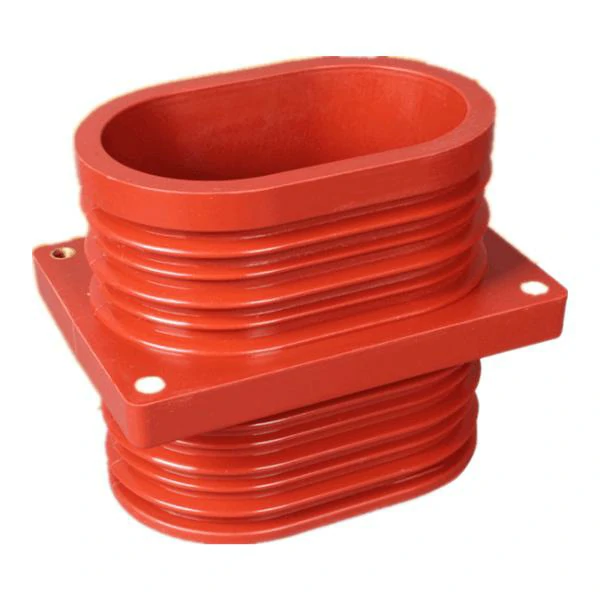
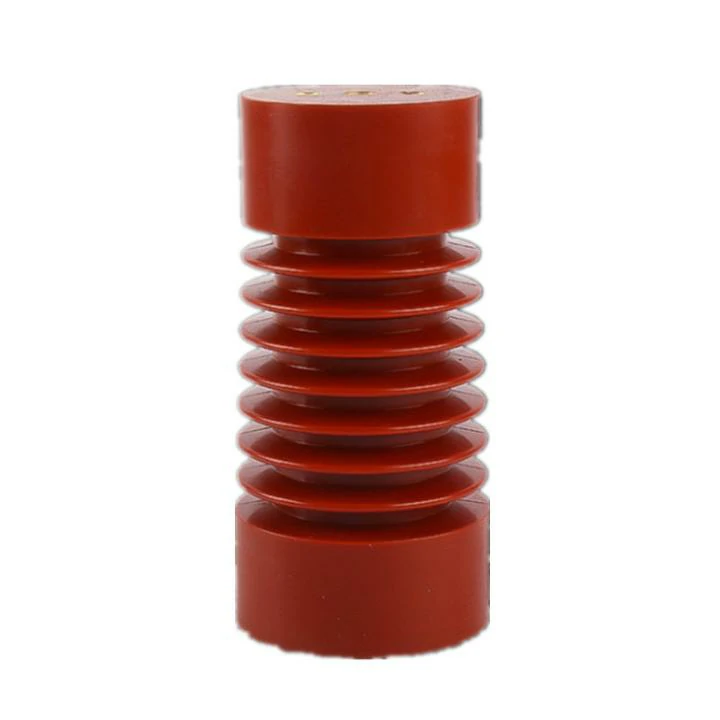
Spout Insulators
Spout Insulators, also known as drop pipe insulators or spout-type insulators, are another specialized category of insulators with distinct design and applications. They are employed in electrical systems to address specific challenges associated with maintaining electrical clearances. Here is an in-depth look at Spout Insulators:
Design and Construction
Spout Insulators are characterized by their elongated, spout-like design. These insulators feature a hollow cylindrical shape with a narrow spout or neck at one end. They are typically constructed from materials like porcelain, glass, or composite polymers.
The spout end of the insulator is attached to the conductor, while the wider end is connected to the supporting structure or cross-arm. This design is critical for ensuring the appropriate distance between the conductor and the supporting structure.
Function and Applications
Spout Insulators serve specific purposes in electrical systems:
- Electrical Clearance Maintenance: Their unique design helps maintain electrical clearances, ensuring that the conductor remains at a safe distance from the supporting structure, even when subjected to mechanical loads or temperature variations.
- Reduced Surface Leakage: The elongated shape reduces the surface leakage current along the insulator, promoting the integrity of the electrical system.
- Corona Ring Integration: Some Spout Insulators feature integrated corona rings, which further help in corona suppression, minimizing power losses and radio interference.
Spout Insulators are commonly used in medium and high voltage overhead power lines, especially where the electrical clearances need to be carefully maintained due to specific environmental conditions or line configurations.
Materials and Insulation Technologies
Both Contact Box and Spout Insulators are constructed from a variety of materials, each offering unique advantages:
- Porcelain: Traditional porcelain insulators are known for their high mechanical strength and resistance to pollution. They are widely used in a range of applications.
- Composite Polymers: Modern insulators are often made from composite polymer materials, such as silicone rubber or epoxy resin. These materials are lightweight, offer excellent electrical insulation properties, and exhibit resistance to environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Glass and Ceramic: Glass and ceramic materials are used for their high dielectric strength, making them suitable for high-voltage applications. They are also known for their resistance to electrical tracking.
Insulator Testing and Quality Assurance
Ensuring the reliability of Contact Box and Spout Insulators is paramount in power distribution systems. These insulators undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance and quality. Testing procedures include:
- Mechanical Tests: Insulators are subjected to mechanical tests to evaluate their structural integrity under various loads, such as tension, compression, and torsion.
- Electrical Tests: Electrical tests assess the insulator’s ability to provide electrical insulation. These tests include flashover voltage testing and puncture voltage testing.
- Environmental Tests: Testing for resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, pollution, and moisture is essential to ensure long-term reliability.
- Corona Performance Testing: For insulators designed for corona suppression, specialized tests are conducted to evaluate their effectiveness in reducing corona discharge.
- Material Analysis: Material properties are analyzed to confirm the suitability of the insulator’s construction materials.
Conclusion
In the intricate world of electrical power transmission and distribution, Contact Box and Spout Insulators play a crucial role in maintaining system integrity, ensuring safety, and providing reliable service. These specialized insulators, with their distinct designs, materials, and applications, contribute to the efficiency and resilience of power distribution networks. Their construction and testing processes are vital in ensuring that they meet the rigorous standards required in the electrical industry. As technology and materials continue to advance, the role of these insulators remains indispensable in the quest for safer, more efficient, and more reliable electrical systems.