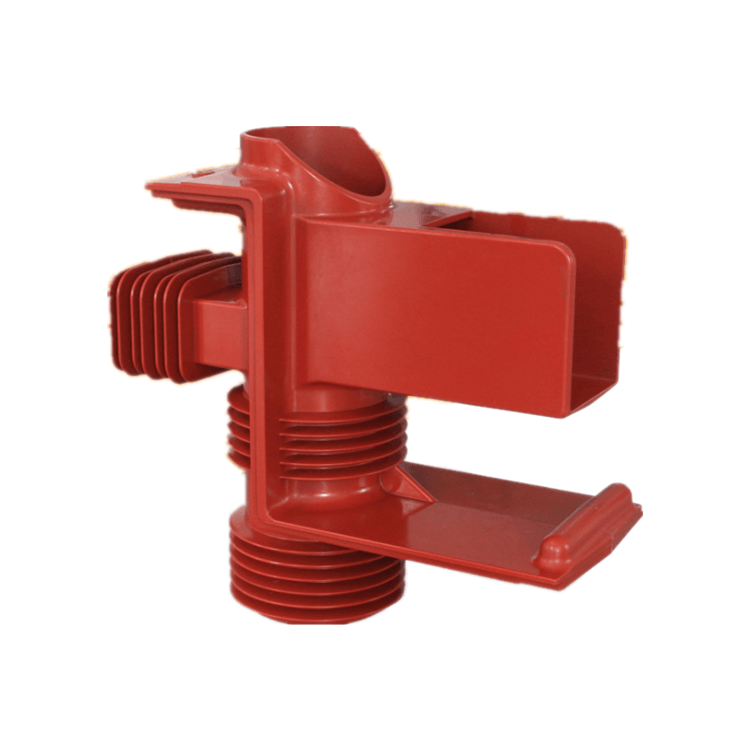
Epoxy bushings and porcelain bushings are essential components used in electrical power distribution and transformer applications. They serve as insulation barriers to protect and support conductors, making them a crucial element of reliable and safe electrical systems. This article aims to provide a comprehensive examination of why epoxy bushings are often considered better than porcelain bushings in various electrical applications. We will explore the material properties, design considerations, advantages, and drawbacks of both types of bushings, along with their specific use cases.
Material Properties
- Epoxy Bushings: Epoxy bushings are manufactured from epoxy resin, a synthetic thermosetting polymer known for its exceptional electrical insulation properties. Some key advantages of epoxy as a material for bushings include:
- High dielectric strength: Epoxy offers superior electrical insulation, making it an excellent choice for high-voltage applications.
- Excellent resistance to moisture and contaminants: Epoxy bushings are less prone to tracking and surface flashover due to their hydrophobic nature.
- Lightweight: Epoxy bushings are significantly lighter than porcelain, simplifying installation and reducing structural stress on equipment.
- Corrosion resistance: Epoxy is highly resistant to chemical corrosion and environmental factors, prolonging the bushing’s lifespan.
- Porcelain Bushings: Porcelain bushings, on the other hand, are made from ceramic materials, often steatite or alumina. Porcelain has its own set of characteristics:
- Good mechanical strength: Porcelain is known for its mechanical robustness, providing adequate support to conductors.
- Adequate electrical insulation: While not as dielectrically strong as epoxy, porcelain still provides adequate electrical insulation for medium-voltage applications.
- Susceptibility to moisture and contaminants: Porcelain is more porous and can absorb moisture and contaminants, potentially leading to tracking and flashover.
- Heavyweight: Porcelain bushings are heavier than epoxy counterparts, which can pose logistical challenges during installation.
Design Considerations
The design of bushings is influenced by various factors, such as voltage level, environmental conditions, and specific application requirements. Let’s delve into how epoxy and porcelain bushings differ in terms of design considerations:
- Voltage Levels:
- Epoxy Bushings: Epoxy bushings are well-suited for high-voltage applications due to their excellent dielectric strength and resistance to partial discharge, making them an ideal choice for transformers and high-voltage circuit breakers.
- Porcelain Bushings: Porcelain bushings are commonly used in medium-voltage applications, where their mechanical strength is advantageous. However, their limited dielectric strength restricts their use in high-voltage applications.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Epoxy Bushings: Epoxy’s resistance to moisture and contaminants makes it ideal for outdoor installations, even in challenging environments with high pollution levels.
- Porcelain Bushings: Porcelain bushings may require more maintenance in polluted or humid areas to prevent surface tracking and flashover.
Advantages of Epoxy Bushings
Epoxy bushings offer several advantages over porcelain bushings:
- Longer Service Life: Epoxy bushings tend to have a longer service life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Reduced Installation Stress: Epoxy bushings are lighter, simplifying transportation, handling, and installation.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: Epoxy’s superior dielectric strength and hydrophobic nature make it an excellent choice for high-voltage applications.
- Resistance to Pollution: Epoxy bushings are highly resistant to environmental pollution, reducing the risk of surface tracking.
- Minimal Maintenance: Epoxy bushings require less maintenance, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
- Design Flexibility: Epoxy bushings offer design flexibility, allowing for various shapes and sizes to meet specific requirements.
Drawbacks of Epoxy Bushings
While epoxy bushings have numerous advantages, they are not without drawbacks:
- Cost: Epoxy bushings are generally more expensive than porcelain bushings, which can be a significant consideration in some applications.
- Vulnerability to UV Radiation: Epoxy materials may degrade over time when exposed to prolonged UV radiation, necessitating additional protective measures in outdoor installations.
Use Cases for Porcelain Bushings
Porcelain bushings still find their niche in specific applications:
- Medium-Voltage Transformers: Porcelain bushings are often used in medium-voltage transformers where their mechanical strength is beneficial.
- Indoor Applications: In indoor settings, where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is limited, porcelain bushings may be a cost-effective choice.
- Low- and Medium-Voltage Circuit Breakers: In low- and medium-voltage circuit breakers, porcelain bushings can provide adequate electrical insulation.
Conclusion
Epoxy bushings and porcelain bushings serve critical roles in electrical power distribution and transformer applications, with each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks. Epoxy bushings are often preferred for high-voltage applications due to their superior electrical properties, longer service life, and resistance to pollution. However, porcelain bushings continue to find utility in medium-voltage applications where their mechanical strength is advantageous and in indoor settings with lower exposure to environmental stressors. The choice between epoxy and porcelain bushings should be made based on specific application requirements, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive understanding of the materials, design considerations, and environmental factors at play.