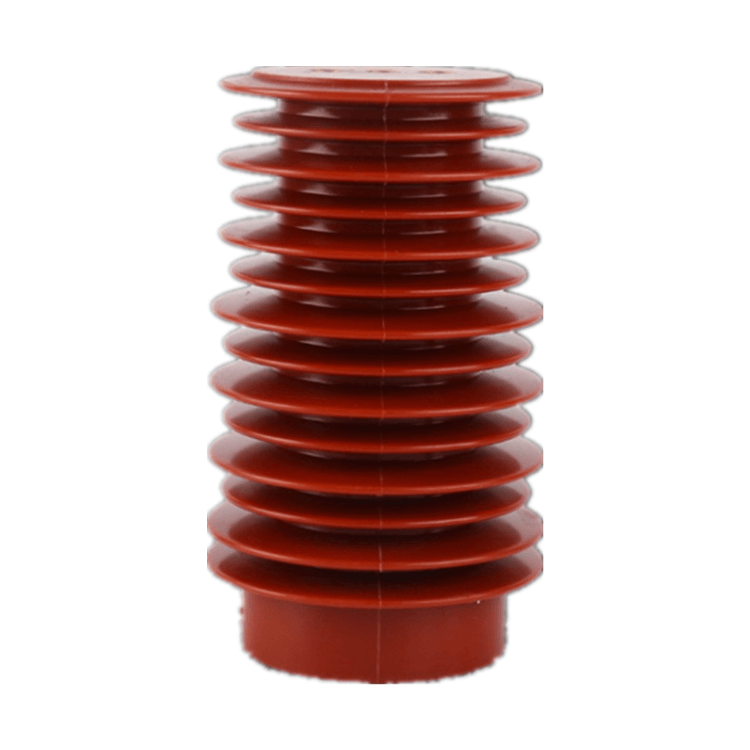
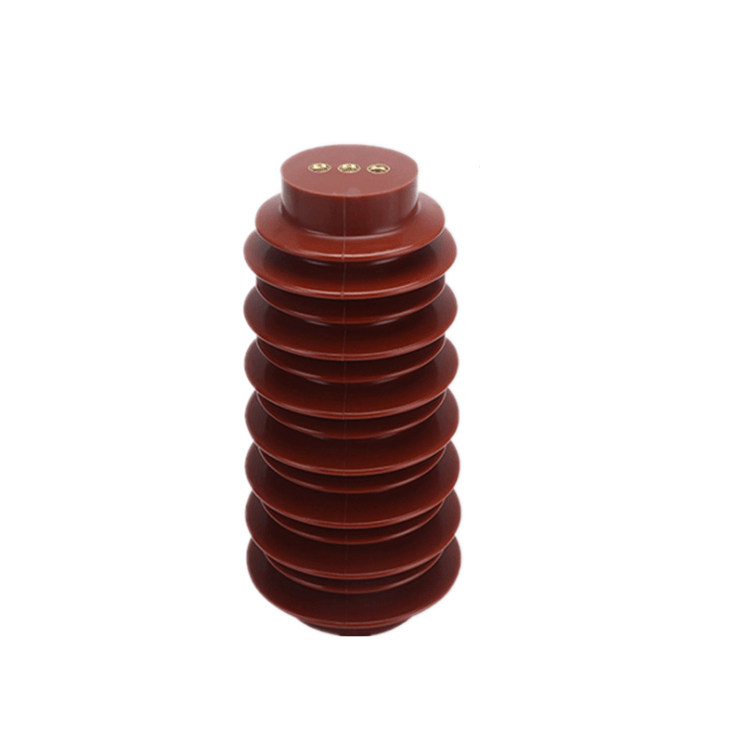
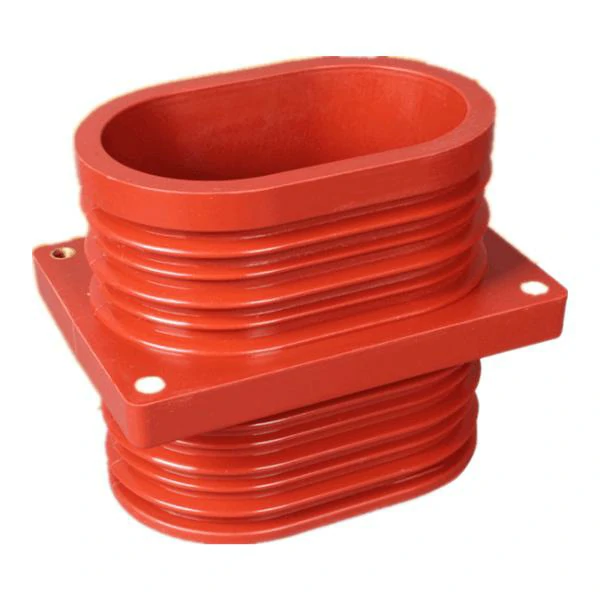
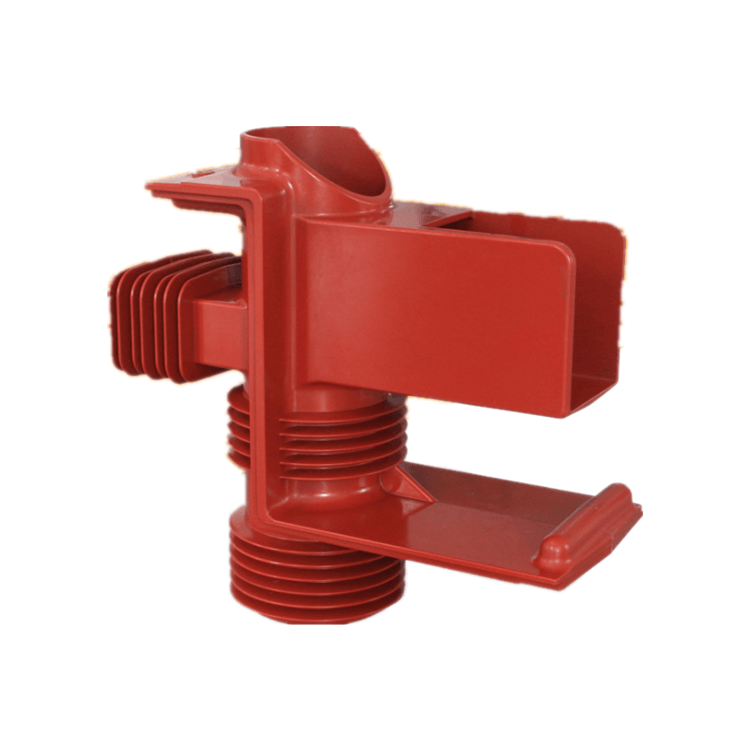
In the realm of electrical engineering, epoxy insulators play a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient and safe transmission of electrical power. These insulators, constructed from epoxy resins, are designed with precision to meet specific requirements, depending on the application. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the multifaceted functions of epoxy insulators in electrical systems, delving into their importance, diverse applications, and the underlying mechanisms that make them an indispensable component in the field.
- Electrical Insulation
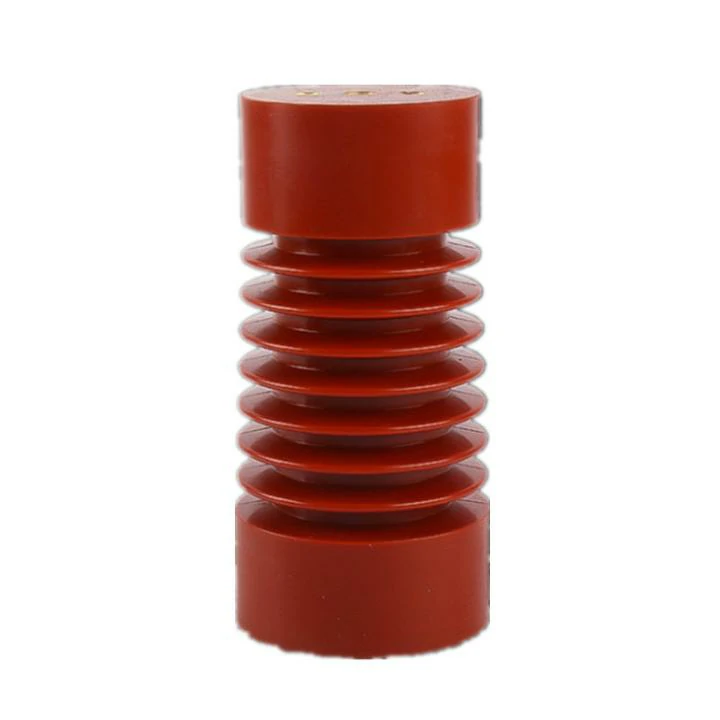
Epoxy insulators are primarily employed as electrical insulators. They serve as a barrier between conductive elements to prevent the flow of electrical current where it is not intended. This function is crucial in power distribution, electronic devices, and various electrical equipment. Epoxy insulators maintain the integrity of electrical circuits, preventing short circuits and ensuring safety.
- High Dielectric Strength
One of the remarkable properties of epoxy insulators is their high dielectric strength. This property allows them to withstand significant electrical voltage without breaking down, making them ideal for use in high-voltage applications such as transformers, switchgear, and substations. Their dielectric strength ensures the safe transmission of electricity over long distances.
- Environmental Resilience
Epoxy insulators are known for their exceptional resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals. They are often exposed to harsh outdoor conditions in electrical installations. The insulators’ ability to withstand these environmental challenges is vital for maintaining the reliability and longevity of electrical systems.
- Mechanical Strength
In addition to their electrical properties, epoxy insulators possess excellent mechanical strength. They can support the weight of overhead conductors, insulating them from the supporting structures. This mechanical strength is crucial in transmission and distribution lines, ensuring the stability and longevity of the system.
- Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion can be a significant issue in electrical systems, especially in coastal or industrial areas. Epoxy insulators are highly corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to corrosive agents is a concern. Their ability to resist corrosion contributes to the longevity of electrical infrastructure.
- Thermal Stability
Epoxy insulators are designed to withstand temperature variations in electrical systems. They have excellent thermal stability, ensuring that they remain effective even in extreme temperature conditions. This property is particularly important in power generation plants and substations, where temperature fluctuations can be substantial.
- Customizability
Epoxy insulators are highly customizable, allowing them to be tailored to specific applications. Electrical engineers can design insulators with varying shapes, sizes, and properties to meet the exact requirements of the system. This versatility ensures that epoxy insulators are a suitable choice for a wide range of applications.
- Pollution Performance
In areas with high pollution levels, such as industrial zones, insulators can become contaminated over time. Epoxy insulators are designed with special sheds and surfaces that minimize the accumulation of pollution and dust. This feature is crucial for maintaining the insulators’ electrical performance and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Light Weight
Compared to traditional ceramic or porcelain insulators, epoxy insulators are relatively lightweight. This characteristic simplifies transportation, installation, and maintenance, reducing the overall cost and effort involved in managing electrical infrastructure.
- Long Service Life
Epoxy insulators are engineered for long service life. Their robust design, resistance to environmental factors, and minimal maintenance requirements contribute to their extended lifespan. This longevity is a cost-effective feature that benefits utilities and operators.
Applications of Epoxy Insulators
Epoxy insulators are widely used in various sectors of the electrical industry. Some of the key applications include:
- High Voltage Power Lines: Epoxy insulators are utilized in high-voltage transmission lines to support conductors and provide electrical insulation.
- Substations: Epoxy insulators are crucial components in substations, where they insulate and support various equipment such as circuit breakers, transformers, and busbars.
- Switchgear: Switchgear, which controls and isolates electrical circuits, often relies on epoxy insulators for their dielectric properties.
- Transformers: Epoxy insulators are used in transformers to insulate windings, ensuring the safe transformation of electrical voltage.
- Outdoor Electrical Equipment: Epoxy insulators are commonly employed in outdoor electrical equipment, including surge arresters and overhead line insulators.
- Electrical Bushings: Epoxy insulators are used as bushings in electrical systems, connecting high-voltage components to lower-voltage circuits.
Mechanism Behind Epoxy Insulators
Epoxy insulators owe their exceptional properties to the molecular structure of epoxy resins and the manufacturing process. Epoxy resins are created by the polymerization of epoxide compounds, forming a cross-linked network of molecules. This network structure provides the insulators with their dielectric strength and mechanical resilience.
The manufacturing process involves casting epoxy resins into molds and then curing them at elevated temperatures. This process ensures that the epoxy resins harden and become solid, creating the final insulator product. The curing process can be adjusted to achieve specific properties, making epoxy insulators highly customizable for various applications.
Conclusion
Epoxy insulators are indispensable components in electrical engineering, serving a multitude of functions critical to the reliable and safe transmission of electrical power. Their high dielectric strength, environmental resilience, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance make them ideal for diverse applications, from high-voltage power lines to substations and transformers. Epoxy insulators offer customizability, pollution performance, and long service life, further enhancing their value in the industry. Understanding the intricate functions and mechanisms behind epoxy insulators is vital for electrical engineers, as they continue to be a cornerstone of modern electrical systems.